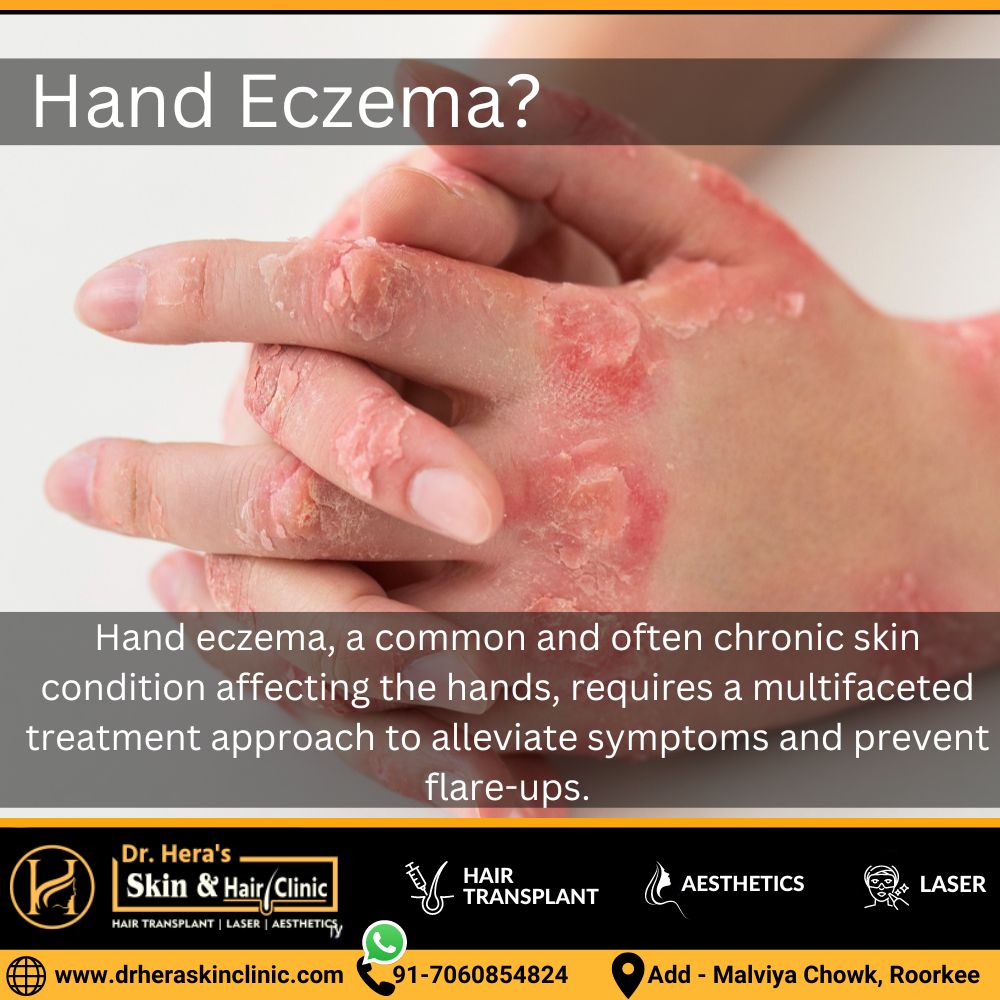
What is hand eczema and treatment?
Hand eczema, a common and often chronic skin condition affecting the hands, requires a multifaceted treatment approach to alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Treatment strategies for hand eczema typically include:
Emollients and Moisturizers:
Regular use of fragrance-free emollients and moisturizers is essential to hydrate the skin, strengthen the protective barrier, and prevent excessive dryness.
Topical Corticosteroids:
Mild to moderate cases of hand eczema often respond well to topical corticosteroids, which reduce inflammation and itching. Dermatologists may prescribe different strengths based on the severity of symptoms.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors:
Non-steroidal creams like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are effective alternatives, particularly for long-term use, as they don’t carry the same risk of skin thinning associated with corticosteroids.
Barrier Repair Creams:
Products containing ceramides and other barrier repair ingredients can help restore and maintain the skin’s natural protective barrier.
Avoidance of Irritants:
Identifying and avoiding irritants and allergens that trigger or worsen hand eczema is crucial. This may involve changes in hand hygiene practices, glove use, and avoidance of harsh chemicals.
Phototherapy:
In some cases, exposure to controlled amounts of ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision may be recommended to manage inflammation and improve symptoms.
Oral Medications:
For severe cases, oral medications like corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed, but their use is typically limited due to potential side effects.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Individuals with hand eczema may benefit from lifestyle adjustments, such as using mild soaps, wearing protective gloves, and practicing proper hand hygiene.
Effective management of hand eczema often requires collaboration with dermatologists to tailor a treatment plan addressing the unique characteristics of the condition and the individual’s lifestyle. Regular follow-ups and adherence to the prescribed regimen are crucial for long-term relief and prevention of recurrences.
Causes of Hand Eczema
Hand eczema can be caused by various factors, and treating it involves addressing these causes:
- Irritants and Allergens: Use gentle soaps and wear gloves to avoid harsh chemicals.
- Dry Skin: Keep your hands moisturized with creams to prevent dryness.
- Contact Dermatitis: Identify allergens through patch testing and use prescribed creams if needed.
- Occupational Factors: Modify work practices, use protective measures like gloves.
- Genetic Predisposition: Follow a good skincare routine and use prescribed creams.
- Stress: Manage stress through relaxation techniques.
- Microbial Infections: Treat infections with antifungal or antibacterial medications.
- Autoimmune Factors: Consult a dermatologist for immune-modulating medications if necessary.
- Weather Conditions: Adjust skincare routines based on weather changes, and use protective clothing.
Working with a dermatologist is key to figuring out what causes your hand eczema and creating a simple, effective treatment plan.
List of Treatments for Hand Eczema
- Emollients and Moisturizers: Regular application of fragrance-free emollients and moisturizers helps maintain skin hydration and prevents dryness.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory creams or ointments that reduce redness and itching, prescribed based on the severity of symptoms.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal creams like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus that suppress immune responses, suitable for long-term use on sensitive areas.
- Avoidance of Irritants: Identification and avoidance of irritants and allergens, such as harsh soaps or chemicals, to prevent flare-ups.
- Barrier Repair Creams: Products containing ceramides and barrier repair ingredients to restore and maintain the skin’s protective barrier.
- Antihistamines: Oral or topical antihistamines to alleviate itching, especially during nighttime itching episodes.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision for managing inflammation and improving symptoms.
- Systemic Medications: In severe cases, oral medications like corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed, typically for short-term use.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Changes in hand hygiene practices, glove use, and the use of mild soaps to minimize exposure to triggers.
- Wet Wrap Therapy: Application of wet bandages over moisturized skin to enhance the absorption of topical treatments, especially in severe cases.
Effective treatment often involves a combination of these approaches tailored to the individual’s condition. Consulting with a dermatologist in Roorkee is crucial for creating a personalized treatment plan and ensuring optimal relief from hand eczema.
